Light Fidelity, or Li-Fi, is a cutting-edge wireless communication technology that has the potential to completely change how we communicate in our ever-digital world. Visible light is used by Li-Fi to transport data, as opposed to radio frequency transmissions, which are used by traditional Wi-Fi. Li-Fi essentially entails the fast modulation of light emitted by LEDs to establish a fast and secure communication channel. With the help of this cutting-edge technology, data transfer speeds in the gigabits per second range might be achieved, exceeding the limits of conventional Wi-Fi.

There has never been a more pressing need for quicker, more dependable, and secure communication than there is in this day and age of expanding data requirements. Because it can take advantage of the visible light spectrum’s enormous untapped capacity, it becomes a very attractive option for meeting the growing demand for effective wireless communication in a variety of contexts, including congested public areas and smart homes.
Table of Contents
What is Li-Fi Technology & How it Works

Li-Fi, which stands for Light Fidelity, is a cutting-edge wireless technology that sends data via visible light. In contrast to conventional radio frequency-based systems like Wi-Fi, it uses LED light modulation to transmit data. The fundamental idea is that binary code is sent by quickly flashing LED lights that are invisible to the human eye. A receiver device then recognizes this flashing and converts the light signals back into data. Li-Fi has a number of benefits, such as faster data transfer speeds, more security (since light signals are limited to a certain region), and less electromagnetic interference.
What is Li-Fi trying to Solve?
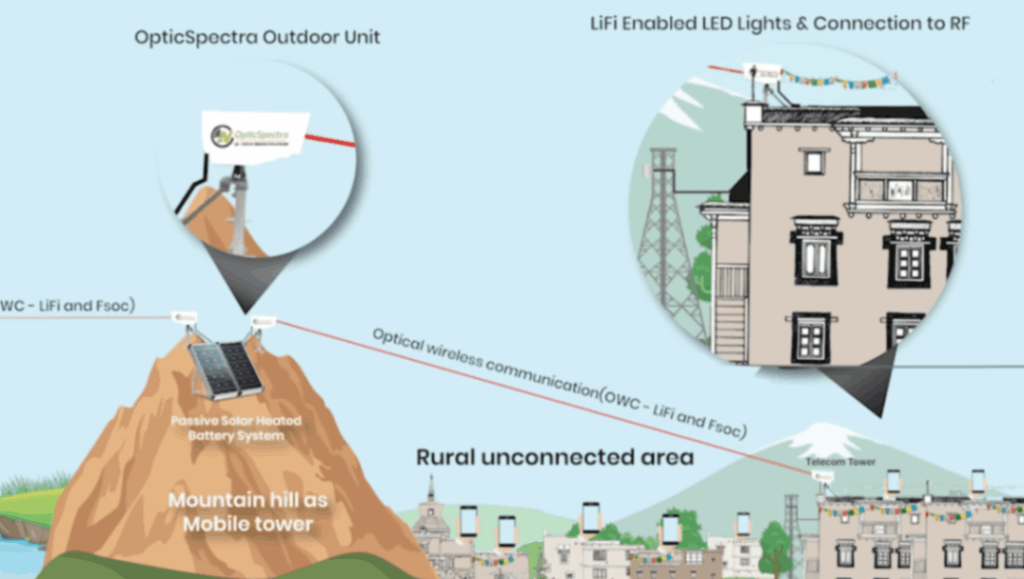
One of the main concerns that Li-Fi aims to address is the issue of spectrum congestion. In traditional wireless communication technologies like Wi-Fi, the radio frequency spectrum is becoming increasingly crowded due to the growing number of connected devices and the demand for higher data transfer rates. This congestion can lead to slower data speeds, dropped connections, and overall reduced network performance.
Li-Fi tackles this problem by utilizing the visible light spectrum for data transmission. Unlike the radio frequency spectrum, the visible light spectrum is vast and largely unregulated, providing more bandwidth for data communication. This enables Li-Fi to offer faster and more efficient data transfer rates, making it a potential solution for environments where spectrum congestion is a significant concern. Li-Fi’s use of light waves allows for a new avenue of wireless communication, offering relief to the limitations faced by traditional radio frequency-based technologies.

Li-Fi addresses this issue by transmitting data over the visible light spectrum. The visible light spectrum offers more bandwidth for data communication because it is larger and mainly unregulated than the radio frequency spectrum. This makes Li-Fi a viable option for situations where spectrum congestion is a major concern since it allows it to provide quicker and more effective data transmission rates. Because Li-Fi uses light waves instead of radio frequencies, it can communicate wirelessly and overcomes some of the drawbacks of standard radio frequency-based technologies.
Advantages of Li-Fi
With a number of benefits, Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) technology is a desirable substitute for or addition to more established wireless communication technologies like Wi-Fi. The following are a few of Li-Fi’s main benefits:
High Data Transfer Rates: Li-Fi has the capacity to carry data at incredibly high speeds, frequently higher than those of conventional Wi-Fi. This is because light waves can be quickly modulated and demodulated, enabling quicker data transmission.

Increased Bandwidth: Li-Fi operates in the visible light spectrum, which is a wider, unregulated bandwidth than the radio frequency spectrum. This lessens the effects of spectrum congestion and permits the operation of multiple devices at once without sacrificing efficiency.
Enhanced Security: Compared to conventional radio frequency-based technologies, it is more secure since it functions inside the boundaries of visible light. An additional layer of protection is provided by the limited range of light signals, which lowers the possibility of illegal entry or data interception.

Reduced Electromagnetic Interference: Li-Fi functions by utilizing light waves as opposed to radio frequency communications, which might be especially helpful in places like hospitals or factories where there is a lot of electromagnetic interference. By doing this, the possibility of signal interference is decreased and overall reliability is increased.
Safety and Health Benefits: Li-Fi does not release any potentially hazardous electromagnetic radiation, in contrast to radio frequency technology. Because of this, it is a safer alternative, addressing issues with long-term exposure and possible health risks linked to extended usage of conventional wireless technology.
Versatility in Deployment: Li-Fi can be used in settings where conventional wireless technologies are difficult to use, like hospitals, airplane cabins, and places with equipment that is susceptible to electromagnetic fields. Because it uses light waves, it is adaptable and useful in a range of situations.
Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient LED lights are frequently utilized for its deployment. These lights are already common in many settings, thus it can take advantage of the lighting infrastructure that already exists, promoting sustainability and energy efficiency.
Potential for Location-based Services: Li-Fi offers applications in retail, navigation, and asset tracking. Its localized data transmission capability can be leveraged for precise indoor positioning and location-based services.
Li-fi v/s Wi-Fi

There are two different wireless communication technologies: Wi-Fi and Li-Fi, each with advantages and disadvantages of its own. Li-Fi has better potential data transfer rates than regular Wi-Fi since it uses visible light instead of radio frequency signals to transmit data. Li-Fi operates in the visible light spectrum, which provides a wider bandwidth, hence mitigating Wi-Fi’s potential spectrum congestion issues. Li-Fi’s confined signal range lowers the possibility of interference and unwanted access, improving security. The requirement for a direct line of sight between the transmitter (an LED light source) and the receiving device, however, currently places limitations on Li-Fi. Wi-Fi, on the other hand, has a wider coverage area and can function well through obstructions.
Both technologies have their uses: Li-Fi is best suited for situations requiring fast, secure, and interference-free communication in small spaces, while Wi-Fi is still the preferred option for general connectivity in a variety of settings. The rivalry and cohabitation of Wi-Fi and Li-Fi add to the changing wireless communication technology landscape.
Possibilities of improvement in Li-fi Technology

LiFi technology has a lot of potential, and there are a lot of opportunities for advancement in the industry thanks to ongoing research and development. Increasing the range and stability of LiFi connections is one way to improve things. In order to enable more flexible deployment scenarios, researchers are investigating ways to get beyond existing constraints, such as the requirement for a direct line of sight between the transmitter and receiver.
By increasing the effectiveness of light modulation and demodulation procedures, LiFi may be able to carry data at even higher speeds, giving it a competitive advantage over more established wireless technologies. Furthermore, improvements in signal processing methods and intelligent algorithms might help LiFi function at its best in difficult settings. The establishment of international protocols for LiFi communication through standardization can aid in the wider use of this technology.
Moreover, advancements in hardware components, including more sophisticated and reasonably priced light-emitting diodes (LEDs), may improve the overall affordability and practicality of LiFi devices. As the technology develops, industry-academia partnerships will probably spur other innovations that open up new avenues and establish LiFi as a major force in wireless communication going forward.
FAQs on Li-Fi Technology
What is the full form of LiFi?
LiFi stands for “Light Fidelity.”
What is the speed of LiFi Technology?
LiFi is approximately 14-15 times faster than WiFi whose speed boasts up to 7 gbps approximately.
Who Invented LiFi?
Professor Harald Haas conceived and launched LiFi technology in a 2011 TEDGlobal lecture. German physicist Harald Haas is an Edinburgh University professor of mobile communications. He gave a demonstration of LiFi, a novel wireless communication system that sends data through visible light. Since then, Professor Haas and his research group have led the way in creating and expanding LiFi technology. Even though Haas was instrumental in making LiFi well known, it’s vital to remember that several engineers and researchers from around the world have contributed to the technology’s advancement and improvement.
What are some projects based on LiFi Technology?
PURELiFi’s Li-1st: Professor Harald Haas co-founded PURELiFi, a business that has led the way in LiFi technology. They created Li-1st, a LiFi product intended for commercial use that uses LED lights to enable high-speed wireless communication.
LiFi for Industry 4.0: Applications of LiFi technology have been researched, especially in manufacturing settings where secure and dependable wireless connectivity is essential for automation and linked equipment.
Smart Cities Initiatives: LiFi technology has been taken into consideration by several smart city projects to create intelligent lighting systems that not only provide high-speed data connectivity but also light up metropolitan areas.
These are the some of projects that have been designed and developed under this technology, the development is not up to the mark as compared to wifi, but still there a hope for the good.
Hope you found the content useful !!
You might also be interested in reading about HOW TO CREATE YOUR OWN AI INFLUENCER IN 2024


1 thought on “Li-Fi vs Wi-Fi: The Battle for Internet Supremacy!”